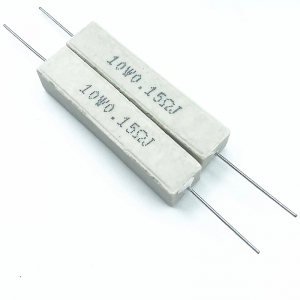
Cement resistors are fixed resistors that use cement materials as insulation and packaging media. This type of resistor is usually wrapped around a ceramic core by a resistance wire or film, and then the entire component is poured or filled in cement to provide good mechanical strength and heat dissipation performance. Cement resistors are widely used in various electronic devices and power systems due to their durability, high temperature resistance, and good stability.
Structure and Materials
The main components of cement resistance include:
Resistor: Usually composed of alloy wire (such as nickel chromium alloy or copper nickel alloy) or thin film resistance materials, these materials have stable resistance characteristics and good heat resistance.
Insulating core: usually made of ceramic material, used to support resistance wires and provide certain insulation performance.
Lead wire: Used to connect the conductive part of a resistor, usually made of copper or tin plated copper, for easy soldering and connection into a circuit.
characteristic
High power endurance: Cement resistors can withstand high power, usually ranging from a few watts to a few hundred watts, and are suitable for high-power applications.
Good heat dissipation performance: Cement encapsulation provides an excellent heat dissipation path, allowing resistors to maintain stability under long-term high load operation.
High mechanical strength: Cement encapsulation endows resistors with high mechanical strength, which can resist vibration and impact, and is suitable for harsh environments.
Good stability: Cement resistance has good temperature stability and time stability, suitable for long-term operation.
Larger size: Compared to other types of resistors, cement resistors are usually larger in size, mainly to meet the needs of heat dissipation and high power.
Cement store owner packaging and dimensions
The packaging of cement resistors usually refers to their external structure and materials, while size refers to their physical size, including length, diameter, lead length, etc. The packaging of cement resistors is mainly composed of cement materials, which not only provide good insulation protection, but also enhance the mechanical strength and heat dissipation performance of the resistors.
Packaging type
The packaging of cement resistors mainly includes the following types:
Standard cement encapsulation: The resistor is completely encapsulated in cement, with only the leads exposed, providing the best mechanical protection and heat dissipation performance.
Open packaging: The resistor body is partially exposed and only partially covered by cement. This packaging may be slightly inferior in terms of heat dissipation, but it is easy to observe the state of the resistor body.
Special packaging: packaging designed for specific applications, which may include special treatments such as waterproofing and explosion-proof.
size
The size of cement resistors varies greatly depending on their power and application scenarios. Generally speaking, the size of cement resistance is directly proportional to its rated power, and the larger the power, the larger the size. Here are some common examples of cement resistance sizes:
Small cement resistor: with a diameter of approximately 5mm to 10mm and a length of approximately 15mm to 30mm, suitable for lower power applications.
Medium cement resistor: with a diameter of approximately 10mm to 20mm and a length of approximately 30mm to 60mm, suitable for medium power applications
Large cement resistor: With a diameter of over 30mm and a length of 100mm or even longer, it is suitable for high-power and high current applications.
The lead length of cement resistors also varies depending on application requirements, usually ranging from a few centimeters to several tens of centimeters. The lead material is usually copper or other conductive metals, and the surface may be tin or nickel plated to enhance corrosion resistance.
When selecting cement resistors, in addition to considering packaging and size, factors such as resistance value, power, error level, temperature coefficient, maximum working voltage, etc. need to be considered to ensure that they meet the requirements of specific applications. Due to the lack of unified standards for the size and packaging of cement resistors, it is best to refer to specific product specifications or data sheets when purchasing to obtain accurate size and packaging information.
application
Cement resistance is widely used in the following fields:
Power supply equipment: used for power filtering, current limiting, and voltage distribution.
Industrial control system: used for motor drive, heater control, and frequency converter.
Audio equipment: Used for load and bias circuits in audio amplifiers.
Automotive Electronics: Used for automotive ignition systems and electronic control units.
Testing and measuring equipment: used for precision measurement and calibration of circuits.
Selection considerations
When choosing cement resistance, the following factors need to be considered:
Rated power: Select the appropriate cement resistor according to the power requirements of the circuit.
Resistance value: Select the appropriate resistance value according to the circuit design requirements.
Error level: Select an appropriate error level based on the accuracy requirements of the circuit
Cement resistors play an important role in specific applications due to their unique performance, especially in situations that require high power and good heat dissipation. However, with the advancement of electronic technology, some new high-power resistors (such as metal oxide varistors, thick film resistors, etc.) are gradually replacing cement resistors in certain fields of application.
Shenzhen Baoxin Chuang Electronics Co., Ltd.
Address: 45th Floor, SEG Plaza, 1002 Huaqiang North Road, Futian District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Website: www.boxintron-ic.com
Tel: +86-0755-8355 3623/8322 8690/8322 8629/8322 8357
Fax: +86-0755-8366 0820
Email: service@boxintron.com
Electronic components with a single expert
Shenzhen Baoxin Chuang Electronics Co., Ltd. is committed to becoming the best IC supplier with single expert and IC agent
Strive to provide customers with one-stop electronic components procurement and IC supporting services
Tel: +86-0755-8355 3623 Fax Fox: +86-0755-8366 0820 Email: service@boxintron.com
Address: Room 4503, 45th Floor, SEG Plaza, 1002 Huaqiang North Road, Futian District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
![Shenzhen Baoxin Chuang Electronics Co., Ltd. [one-stop type of electronic components with one-only original authentic] Shenzhen Baoxin Chuang Electronics Co., Ltd. [one-stop type of electronic components with one-only original authentic]](templates/web/images/logo.png)